The High Price Of High Fuel Efficiency
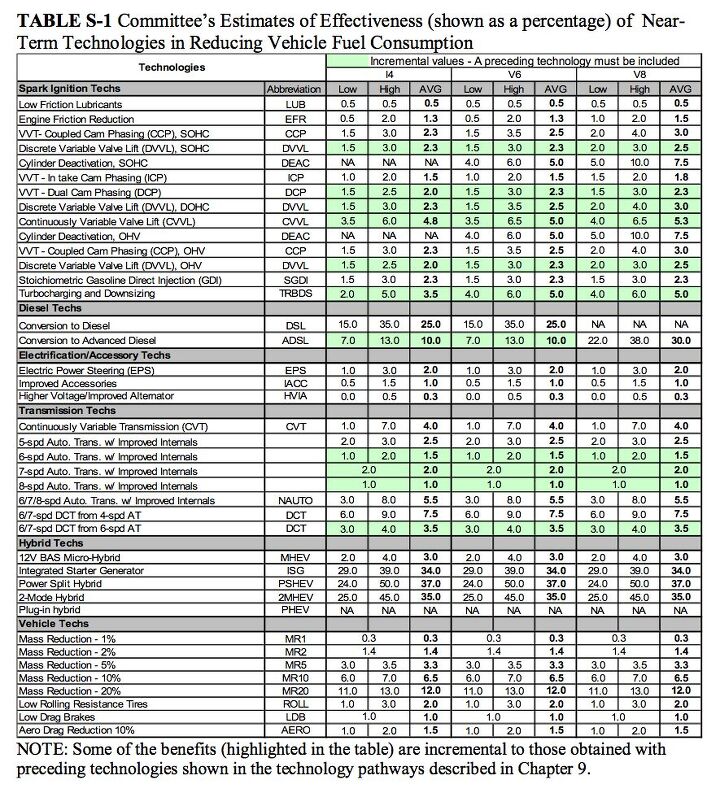
The National Academy of Science’s National Research Council has released a comprehensive report on fuel-saving technologies and their associated costs [full report available online here, summary in PDF format here], and it’s data-licious. Just about every currently-available (within the next five years) efficiency-improving technology was assessed, not just for efficiency gains, but for cost as well… but let’s wait on the cost part for just one moment. Above, you can see the study’s findings in regard to efficiency gain available through various near-term technologies, as applied to vehicles with 4, 6 and 8-cylinder engines. It should come as no surprise to find that conversion to Hybrids, diesels and dual-clutch or continuously-variable transmissions offer some of the greatest benefits… but what about those costs?
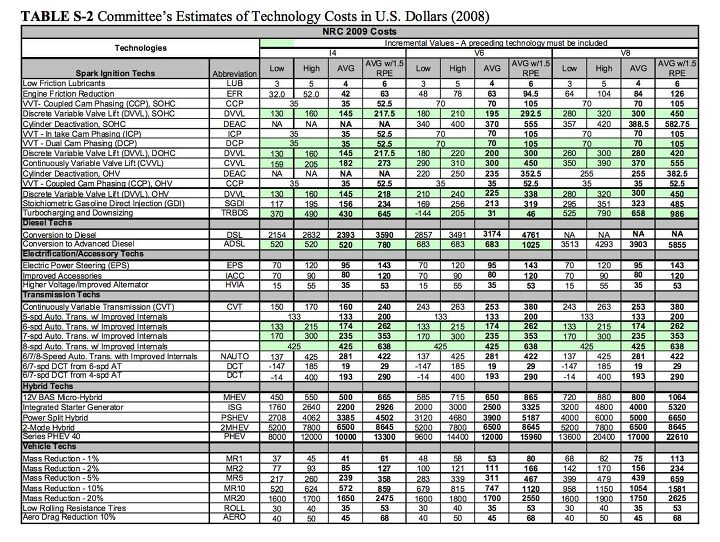
Well, will you look at that? All the silver bullets are expensive. Don’t you just hate it when that happens? The study’s presser summarizes:
Adopting the full combination of improved technologies in medium and large cars and pickup trucks with spark-ignition engines could reduce fuel consumption by 29 percent at an additional cost of $2,200 to the consumer. Replacing spark-ignition engines with diesel engines and components would yield fuel savings of about 37 percent at an added cost of approximately $5,900 per vehicle, and replacing spark-ignition engines with hybrid engines and components would reduce fuel consumption by 43 percent at an increase of $6,000 per vehicle.
Meanwhile, don’t even think about think about camless valves, HCCI, “advanced diesels,” plug-in hybrids, diesel hybrids, EVs or hydrogen fuel cells. The report puts all of those technologies outside of the five-year window for this report, and notes that
some of these technologies will remain perennially 10 to 15 years out beyond a moving reference.
For now, the studying continues, as the NAS builds more sophisticated models around either real or theoretical “class defining vehicles” to help them understand how integrating these technologies can cause beneficial and harmful interactions. In the meantime, the report’s strongest conclusion is that EPA and CAFE abandon MPG in favor of gallons per 100 miles and improve testing procedures because certain technologies ( probably start-stop systems, among others) do not register realistic energy savings. We can certainly agree with that much.
This report may have uncovered more questions than answers, but it’s an in-depth look at the options and trade-offs available to contemporary product planners. THe methodology, though imperfect, is well-explained. If fuel economy catches your attention, but pie-in-the-sky futuretech turns you off, this report is required reading.
More by Edward Niedermeyer
Latest Car Reviews
Read moreLatest Product Reviews
Read moreRecent Comments
- Theflyersfan I used to love the 7-series. One of those aspirational luxury cars. And then I parked right next to one of the new ones just over the weekend. And that love went away. Honestly, if this is what the Chinese market thinks is luxury, let them have it. Because, and I'll be reserved here, this is one butt-ugly, mutha f'n, unholy trainwreck of a design. There has to be an excellent car under all of the grotesque and overdone bodywork. What were they thinking? Luxury is a feeling. It's the soft leather seats. It's the solid door thunk. It's groundbreaking engineering (that hopefully holds up.) It's a presence that oozes "I have arrived," not screaming "LOOK AT ME EVERYONE!!!" The latter is the yahoo who just won $1,000,000 off of a scratch-off and blows it on extra chrome and a dozen light bars on a new F150. It isn't six feet of screens, a dozen suspension settings that don't feel right, and no steering feel. It also isn't a design that is going to be so dated looking in five years that no one is going to want to touch it. Didn't BMW learn anything from the Bangle-butt backlash of 2002?
- Theflyersfan Honda, Toyota, Nissan, Hyundai, and Kia still don't seem to have a problem moving sedans off of the lot. I also see more than a few new 3-series, C-classes and A4s as well showing the Germans can sell the expensive ones. Sales might be down compared to 10-15 years ago, but hundreds of thousands of sales in the US alone isn't anything to sneeze at. What we've had is the thinning of the herd. The crap sedans have exited stage left. And GM has let the Malibu sit and rot on the vine for so long that this was bound to happen. And it bears repeating - auto trends go in cycles. Many times the cars purchased by the next generation aren't the ones their parents and grandparents bought. Who's to say that in 10 years, CUVs are going to be seen at that generation's minivans and no one wants to touch them? The Japanese and Koreans will welcome those buyers back to their full lineups while GM, Ford, and whatever remains of what was Chrysler/Dodge will be back in front of Congress pleading poverty.
- Corey Lewis It's not competitive against others in the class, as my review discussed. https://www.thetruthaboutcars.com/cars/chevrolet/rental-review-the-2023-chevrolet-malibu-last-domestic-midsize-standing-44502760
- Turbo Is Black Magic My wife had one of these back in 06, did a ton of work to it… supercharger, full exhaust, full suspension.. it was a blast to drive even though it was still hilariously slow. Great for drive in nights, open the hatch fold the seats flat and just relax.Also this thing is a great example of how far we have come in crash safety even since just 2005… go look at these old crash tests now and I cringe at what a modern electric tank would do to this thing.
- MaintenanceCosts Whenever the topic of the xB comes up…Me: "The style is fun. The combination of the box shape and the aggressive detailing is very JDM."Wife: "Those are ghetto."Me: "They're smaller than a Corolla outside and have the space of a RAV4 inside."Wife: "Those are ghetto."Me: "They're kind of fun to drive with a stick."Wife: "Those are ghetto."It's one of a few cars (including its fellow box, the Ford Flex) on which we will just never see eye to eye.

































Comments
Join the conversation
Don't one technology is better than another until the three are three or less cylinders: http://www.autocar.co.uk/News/NewsArticle.aspx?AR=250346 I love getting 69-71 mpg on my 2-cylinder Suzuki SV650 which has enough power to be fun and get out of the way of distracted drivers in 300 hp FWD sedans.
The best way to improve non-commercial motor vehicle fuel economy would be to apply a weight tax. This would be a simple way to provide a disincentive for people to drive SUVs and heavy cars, and it would be more politically possible than. http://hubpages.com/hub/How-to-Reduce-CO2-Emissions-from-Non-commercial-Motor-Vehicles