#Connectivity
Driving Dystopia: Automakers Are Selling Your Driving Data to Insurance Companies
A recent report from The New York Times has accused automakers of selling customer driving data to insurance firms. While this is something many drivers had already been made aware of since the implementation of connected vehicles, the outlet claims that the amount of data has ramped up to a staggering degree. Not only is the amount of data being shared staggering, so is the specificity and degree to which it’s impacting people’s insurance rates.
The report focuses on LexisNexis’ “Risk Solutions” program formerly dedicated to keeping track of accident reports and moving violations. However, the division has expanded dramatically over the years and now oversees just about every scrap of relevant data modern vehicles can accumulate about you.
Yay or Nay? Volvo Launches Accident Ahead Alert Service
Volvo is introducing a new feature that alerts drivers of accidents reported on the road ahead. With similar services available for free on select phone apps, many of which can be integrated with your vehicle’s infotainment display, Volvo’s offering doesn’t sound incredibly novel on its face. But it’s leveraging real-time data from government-operated traffic management centers via the automobile’s proprietary user interface, technically making the feature the first of its kind within the automotive industry.
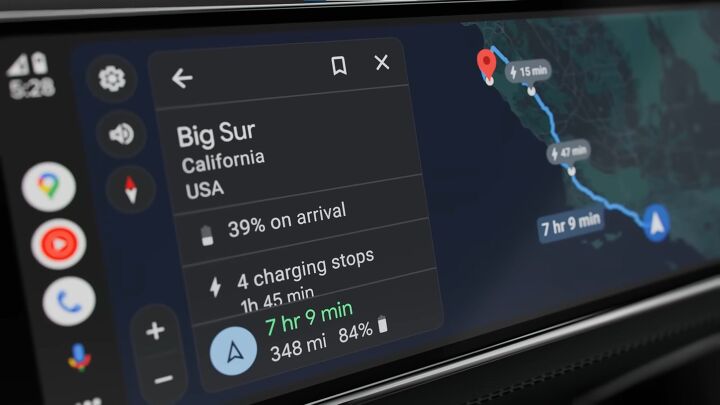
Google Claims Android Auto Will Become Safer and Smarter After Update
Google has announced plans to update Android Auto to reduce the time drivers are required to look at screens. This includes the obligatory mention of leveraging artificial intelligence. But the phrase has become a blanket term for any advanced computing integrated into other systems, meaning we have to dig a little deeper to understand what AI brings to the table. While Google hasn’t gotten overly specific, it has said it wants to place an emphasis on improving safety.
How Much Privacy Do You Really Have In Modern Vehicles?
Whenever the issue of vehicular privacy comes up, the discussion almost immediately pivots to individuals either defending or condemning the status quo. But this often happens without either side of the argument having a firm understanding of how much information is actually being obtained inside today’s automobiles.
While we’ve covered the topic frequently, articles have typically focused on specific issues rather than overall scope. But things are different this time, with the Mozilla Foundation recently issuing a study trying to assess just how far-reaching the automotive industry’s quest for data has become.
Driving Dystopia: Companies Are Getting Serious About Vehicle-to-Infrastructure Connectivity
Before connected vehicles had become ubiquitous, numerous companies suggested that they would be networked into roadway infrastructure to improve safety and decrease traffic congestion. The concept even became a keystone issue for lobbyists trying to convince lawmakers to create regulations favorable to autonomous cars.
But it never manifested due to just how ambitious the overarching concept happened to be. The relevant technologies were still in their infancy and would require years of collaboration between multiple industries and various government agencies before anything got off the ground. However, things are reportedly starting to change. Pilot programs are being implemented on public streets, companies are working on the necessary hardware, and the U.S. government is asking for more with cash in hand.
Mercedes Putting Performance Behind Digital Paywall for EQ EVs
Mercedes-Benz has made some changes to its commercial EQ website and now appears to be offering an “Acceleration Increase” subscription that boosts performance in exchange for an additional $1,200 per year. However it doesn’t do this by installing new hardware, Mercedes is just remotely goosing the powertrain it already has for massive gains. Though this also means it’s artificially limiting the output of those very same vehicles until its customers cave in and allow themselves to be locked into an annual fee.
BMW and Amazon Partner Up to Swipe Your Data
Amazon Web Services and BMW are reportedly joining forces to establish a new cloud-based software designed to deliver and manage the data amassed by connected vehicles – which is great news if you happen not to value your privacy.
Hyundai Announces Future Roadmap: Subscriptions, Software Defined Vehicles, and OTA Updates
Hyundai Motor Group – which includes Hyundai, Kia, and Genesis – has announced a comprehensive plan for its products from 2025 onward with the key components being perpetual connectivity, subscriptions, and software-defined automobiles. It sounds benign but actually represents a major shift in the way the company operates by calling for widespread platform standardization and leaning into novel revenue streams reliant on vehicles existing on its corporate network.
NHTSA Updating Guidance for Connected Cars, Cybersecurity
Despite having a formal mission objective to “save lives, prevent injuries, and reduce vehicle-related crashes,” the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has been shifting some of its focus toward automotive connectivity over the last few years. In fact, the agency has recently updated its guidance for vehicle cybersecurity – which was originally penned in 2016.
While this raises questions about the true role of the NHTSA, most government regulators have been flexing their muscles as new automotive technologies lacking clearly defined directives become increasingly commonplace. Besides, the safety agency has at least managed to tie its cybersecurity guidance (which is currently voluntary) to hacking concerns that could affect how the affected car behaves and how that might translate into physical harm for those on the road.
Tesla to Begin Charging Subsription for Connectivity Services
Not to be outdone by the likes of BMW and Volkswagen Group, Tesla has decided to begin linking its connected services to a subscription-based payment plan. German automakers may be careening headlong into an era where you have to pay a monthly fee just to activate already installed hardware like heated seats. Though Tesla remains the master at conning customers into overpaying for nebulous features and we need only look at the Full-Self Driving suite, that has yet to manifest into genuine vehicular autonomy and just keeps getting more expensive, for an example.
While the standard connectivity package has always been free for the vehicle's lifespan, Big T is now saying that's only going to be true for the first eight years of ownership. The rationale here is that automotive companies have to continue supporting connectivity services and that there needs to be something to help offset that ongoing financial investment.
Digital License Plates Gaining Traction in U.S.
Michigan has opted to allow digital license plates, making it the third state – after California and Arizona – to give them legal backing. The state’s legislature passed the necessary laws in 2019, making it legal for vehicles registered in Michigan to utilize digital vehicle identification while traveling throughout the rest of the nation. But the company that produces them, Reviver, has only just recently found itself in a position to furnish them.
Whoops: Some Seattle-Area Mazdas Are Stuck Listening to NPR
There’s a gaggle of Mazda owners in Seattle, Washington, that have reportedly been stuck listening to National Public Radio (NPR) over the last few weeks. The manufacturer has addressed the problem, saying the local affiliate had broadcast images files with no extension causing an issue on some 2014-2017 Mazda vehicles with older HD radio software. This effectively bricked the infotainment system on some vehicles, locking them into listening to NPR and out of literally everything else.
U.S. Regulators 'Crack Down' on Tesla for Letting Customers Play Video Games
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has launched a formal investigation into 580,000 Tesla vehicles sold since 2017 that allowed customers to play video games inside the vehicle. The company has allowed users to play a variety of games while vehicles are in park, some of which allowed drivers to use the steering wheels and pedals as part of the controls, for quite some time. But an over-the-air software update permitted a few of them to be launched while the car was in motion by the passenger in the summer of 2021. Called “Passenger Play,” the service was limited to games that only used touchscreen controls.
It’s since been axed, however, regulators have taken an interest following some manufactured outrage. The NHTSA has faulted the feature as part of the ongoing distracted-driving problem in an attempt to link it to its crusade against Autopilot. The agency has launched a preliminary investigation into 580,000 Tesla Model 3, S, X, and Y vehicles to determine if they’re attention-sucking deathtraps.
Can Automakers Really Cash In on Connectivity and Subscription Schemes?
A little over a decade ago, it seemed like everyone I knew was abandoning cable packages for online streaming services. They were cheaper, on-demand, and offered more choices with fewer advertisements. But as the years progressed, companies stopped selling their media to a handful of online video platforms and started building their own. Programming became more transient and isolated, forcing consumers to buy into additional subscription services. We’ve since hit a point where the overall consumer experience has diminished and grown more expensive, despite the steady influx of competition.
While automakers have been dabbling with subscription services of their own, their earliest attempts turned out to be such overwhelmingly bad deals that the public refused to play along. But they’re not giving up that easily. Industry players have been trying to figure out ways to charge customers indefinitely for years and are starting to settle upon subscription packages that can unlock hardware that’s already been installed into the vehicle or add software that can be downloaded via over-the-air (OTA) updates. Love or hate it, vehicular connectivity has opened up the door for new sources of revenue and businesses everywhere are eager to take advantage — with most companies projecting exceptionally healthy profits for the years ahead.
Report: The End of 3G Could Leave Your Vehicle With Fewer Features
When people started burning down 5G towers in fear, the practice seemed a little misguided. But if you happen to be the owner of a connected automobile, there’s a chance you’ll be wishing enough of them had been taken down to delay those low-latency spires from becoming the default broadcasting network.
While you were probably aware that 3G cellular networks will be shut down in the U.S. next year so the telecom industry can focus in on 5G, you may not have been hip to the fact that this could totally nullify the connected features inside of your car. Unfortunately, loads of automobiles manufactured the early days of phone pairing and internet integration won’t be able to make the journey into 5G like the new phone or tablet you purchased. Worse yet, there are even some modern vehicles that are about to become a lot less feature rich with companies that have no intention of offering updates.



























Recent Comments