#fcc
Driving Dystopia: Companies Are Getting Serious About Vehicle-to-Infrastructure Connectivity
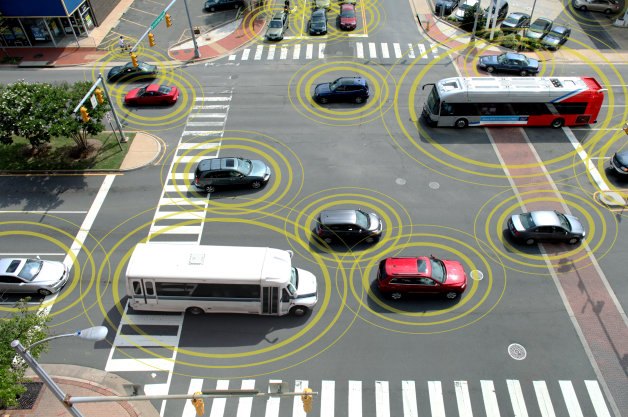
Before connected vehicles had become ubiquitous, numerous companies suggested that they would be networked into roadway infrastructure to improve safety and decrease traffic congestion. The concept even became a keystone issue for lobbyists trying to convince lawmakers to create regulations favorable to autonomous cars.
But it never manifested due to just how ambitious the overarching concept happened to be. The relevant technologies were still in their infancy and would require years of collaboration between multiple industries and various government agencies before anything got off the ground. However, things are reportedly starting to change. Pilot programs are being implemented on public streets, companies are working on the necessary hardware, and the U.S. government is asking for more with cash in hand.
NHTSA Updating Guidance for Connected Cars, Cybersecurity
Despite having a formal mission objective to “save lives, prevent injuries, and reduce vehicle-related crashes,” the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has been shifting some of its focus toward automotive connectivity over the last few years. In fact, the agency has recently updated its guidance for vehicle cybersecurity – which was originally penned in 2016.
While this raises questions about the true role of the NHTSA, most government regulators have been flexing their muscles as new automotive technologies lacking clearly defined directives become increasingly commonplace. Besides, the safety agency has at least managed to tie its cybersecurity guidance (which is currently voluntary) to hacking concerns that could affect how the affected car behaves and how that might translate into physical harm for those on the road.
Whoops: Some Seattle-Area Mazdas Are Stuck Listening to NPR
There’s a gaggle of Mazda owners in Seattle, Washington, that have reportedly been stuck listening to National Public Radio (NPR) over the last few weeks. The manufacturer has addressed the problem, saying the local affiliate had broadcast images files with no extension causing an issue on some 2014-2017 Mazda vehicles with older HD radio software. This effectively bricked the infotainment system on some vehicles, locking them into listening to NPR and out of literally everything else.
Report: The End of 3G Could Leave Your Vehicle With Fewer Features
When people started burning down 5G towers in fear, the practice seemed a little misguided. But if you happen to be the owner of a connected automobile, there’s a chance you’ll be wishing enough of them had been taken down to delay those low-latency spires from becoming the default broadcasting network.
While you were probably aware that 3G cellular networks will be shut down in the U.S. next year so the telecom industry can focus in on 5G, you may not have been hip to the fact that this could totally nullify the connected features inside of your car. Unfortunately, loads of automobiles manufactured the early days of phone pairing and internet integration won’t be able to make the journey into 5G like the new phone or tablet you purchased. Worse yet, there are even some modern vehicles that are about to become a lot less feature rich with companies that have no intention of offering updates.
Auto Industry Squabbles With FCC, Promises to Use Allocated Bandwidth
Way back in 1999, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) set aside frequencies so automobiles could communicate with surrounding infrastructure. Concepts included traffic monitoring, speed mitigation, data analysis, new opportunities for law enforcement, and improved self-driving capabilities. The industry never made much use of it, focusing instead on more independent autonomous vehicles that wouldn’t need help from the surrounding world, and which could simply communicate with each other (and manufacturer data centers) using existing wireless networks.
Annoyed that automakers had barely touched the bandwidth allocated to them, the FCC suggested handing it over to someone else in 2019. In response, the Alliance for Automotive Innovation (AAI) promised that if the commission voted to uphold the status quo on the 5.9-GHz band, the automotive sector would install 5 million vehicle-to-everything (V2X) radios on vehicles and roadside infrastructure over the next five years.
Attention Automakers: Ajit Pai is Not Your Friend
Two decades ago, the Federal Communications Commission decided to allocate a portion of the radio frequency spectrum for Dedicated Short Range Communications ( DSRC). The plan was to utilize that slice of the airwaves for ultra-modern automotive technologies relating to vehicle-to-vehicle and/or vehicle-to-infrastructure communications. Unfortunately, there hasn’t been a whole lot of activity on those channels.
The automotive industry was concerned it might need dedicated frequencies for use in autonomous-vehicle applications or some, yet unknown, technological advancement. But cable companies are annoyed that it’s being “wasted” and have started to antsy. They’ve asked the FCC to revoke carmakers’ exclusive rights to the frequencies and reallocate the majority of the 5.9-GHz band to the Wi-Fi systems that currently carry internet traffic for cable customers.
Hoping to encourage the commission to see things its way, Ford took FCC Chairman Ajit Pai out for a ride in an extra-special F-150 to plead its case. However, I feel like I can already predict whose side he’s going to take on this issue… and it isn’t going to be the automakers’.
Right of the Dial: FCC May Open Automotive Safety Radio Frequency for Telecom Use
The Federal Communications Commission has decided to review how the radio spectrum intended for wireless communications should be divided. While a seemingly normal part of its duties, the reassessment could open up a part of the spectrum that was previously reserved for automotive applications. The super-high 5.9 GHz frequency reserved for cars was deemed important because it would help enable low-power connectivity in remote and high-density areas, allowing for vehicles to more reliably transmit information between each other and the infrastructure. This was framed by the interested parties as essential for helping to develop safe, autonomous driving systems but it could likely also work to aid any data-based services they offer in the future.
Meanwhile, cable companies, the telecom industry, and internet service providers (ISPs) don’t think it’s fair that automakers are getting their own slice of bandwidth when they’re not even using it yet. Carmakers have been working on vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V), vehicle-to-infrastructure, and dedicated short-range communication (DSRC) for years without much in the way of consumer applications.
FCC Prepares Repeal On Net Neutrality: Autonomous Car Victory or Orwellian Nightmare?
You’ve no doubt heard about net neutrality over the last few years. But, in case you haven’t, net neutrality is the principle that forces Internet service providers to treat all data on the Internet equally. It forbids them from discriminating on subject matter or charging different fees based upon the user, site content, website, platform, application, or method of delivery. Essentially, it makes the internet into a tap where you pay one flat fee for access to all content.
That could soon change. On Tuesday, the chairman of the Federal Communications Commission announced plans to repeal the landmark neutrality order from 2015. FCC head Ajit Pai, a Republican appointed by President Donald Trump in January, said last year that he believed net neutrality’s “days were numbered.”
Pai has been criticized for being overly supportive of telecom companies. But a few automakers support his cause, as some of the FCC’s regulations have been at odds with autonomous car development.
FCC Makes Room on the Airwaves for Autonomous Vehicles
Despite the Federal Communications Commission making a mess of net neutrality right now, it remains capable of serving corporate interests and the general public simultaneously. On Thursday, the FCC quintupled the allocation of the radio spectrum used for motor vehicle and aircraft radar systems to help avoid crashes.
While the majority of autonomous cars also use laser guidance and a complex network of cameras to navigate, radar remains an integral component. Presently, the 1 GHz of spectrum set aside in 1995 has been sufficient for self-driving vehicles using adaptive cruise control or automatic emergency braking. But we’re about to enter an era of connected cars that will be required to “speak” to one another, and those vehicles will need plenty of space to talk — 5 GHz of bandwidth, to be precise.
A Detroit/Silicon Valley War Is In The Air(waves)
The Alliance of Automobile Manufacturers on Thursday sent a letter to the heads of the Federal Communications Commission, U.S. Department of Transportation and U.S. Department of Commerce, urging the groups to keep dedicated a frequency spectrum for future car communication systems.
The spectrum, which is between 5.850 GHz and 5.925 GHz, was allotted to automakers for car-to-car communication and road-to-car communication. Telecommunications and Wi-Fi industry officials have asked to share the spectrum.
“Um, no,” in the nicest possible way, from the Alliance:
We are committed to finding the best path forward to protect the development and deployment of advanced automotive safety systems while also considering the need for additional unlicensed spectrum to meet the increasing demand for wireless broadband Internet services.
Motorist Faces $48,000 In Fines For Mounting Cellular Signal Jammer In Car
Network World is reporting that a Florida man who installed a cellular telephone jamme r in the back seat of his Toyota Highlander is facing $48,000 in fines levied by the Federal Communications Commission. The FCC alleges that one Jason R Humphreys of Seffner, FL regularly used the device during his daily commute and that he originally installed it more than two years ago. When questioned about his reasoning, Mr. Humphreys told officials that he installed the jammer in order to prevent people in the cars around him from using their cell phones while driving – something that is, by the way, totally legal in the state of Florida with or without a hands-free device.
























Recent Comments